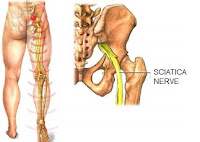
It is usually a pain that results from compressing the nerves of a discoid or bones on the spine. Sciatica or sciatica pain refers to the pain that develops from the bottom of the back to the hips and along the nerves that descend from either head. Typically, the sciatica affects only one side of the body. Often a dyspnea on the spine or a compression of the nerves of the bone is a resultant pain. This condition also causes inflammation and numbness in the affected leg. Some of the sciatic-associated aches may be very severe. However, in most cases complaints are resolved by conservative treatment for several weeks. Surgery after six weeks of treatment in severe pain will reduce the pressure on the nerve.
What is Sciatica
There is a nerve in the human body called sciatic. This pain caused by the nerve is called sciatica.
Should a doctor be consulted for sciatica pain?
The sciatic pain at a slight degree usually passes by itself over time. With home self-care methods, do not lighten your symptoms or see a doctor if the pain lasts longer than a week, worsens or becomes exacerbated.
If you experience sudden and severe pain in the lower part of the waist or numbness and muscle weakness in the legs. When a pain, like a traffic accident, occurs after a severe injury, When you have trouble with bowel or bladder control; Emergency medical assistance is required.
 It is usually a pain that results from compressing the nerves of a discoid or bones on the spine. Sciatica or sciatica pain refers to the pain that develops from the bottom of the back to the hips and along the nerves that descend from either head. Typically, the sciatica affects only one side of the body. Often a dyspnea on the spine or a compression of the nerves of the bone is a resultant pain. This condition also causes inflammation and numbness in the affected leg. Some of the sciatic-associated aches may be very severe. However, in most cases complaints are resolved by conservative treatment for several weeks. Surgery after six weeks of treatment in severe pain will reduce the pressure on the nerve.
It is usually a pain that results from compressing the nerves of a discoid or bones on the spine. Sciatica or sciatica pain refers to the pain that develops from the bottom of the back to the hips and along the nerves that descend from either head. Typically, the sciatica affects only one side of the body. Often a dyspnea on the spine or a compression of the nerves of the bone is a resultant pain. This condition also causes inflammation and numbness in the affected leg. Some of the sciatic-associated aches may be very severe. However, in most cases complaints are resolved by conservative treatment for several weeks. Surgery after six weeks of treatment in severe pain will reduce the pressure on the nerve. It is usually a pain that results from compressing the nerves of a discoid or bones on the spine. Sciatica or sciatica pain refers to the pain that develops from the bottom of the back to the hips and along the nerves that descend from either head. Typically, the sciatica affects only one side of the body. Often a dyspnea on the spine or a compression of the nerves of the bone is a resultant pain. This condition also causes inflammation and numbness in the affected leg. Some of the sciatic-associated aches may be very severe. However, in most cases complaints are resolved by conservative treatment for several weeks. Surgery after six weeks of treatment in severe pain will reduce the pressure on the nerve.
It is usually a pain that results from compressing the nerves of a discoid or bones on the spine. Sciatica or sciatica pain refers to the pain that develops from the bottom of the back to the hips and along the nerves that descend from either head. Typically, the sciatica affects only one side of the body. Often a dyspnea on the spine or a compression of the nerves of the bone is a resultant pain. This condition also causes inflammation and numbness in the affected leg. Some of the sciatic-associated aches may be very severe. However, in most cases complaints are resolved by conservative treatment for several weeks. Surgery after six weeks of treatment in severe pain will reduce the pressure on the nerve.
Comments
Post a Comment